ADAS
Introduction
An autonomous vehicle is a vehicle that can operate without the assistance of a human. It can carry out specialized functions by sensing and responding to external conditions and surroundings using superior and built-in car programs.
The autonomous vehicle, also known as self-driving cars, have propelled significant shifts in automation and connectivity. The internet, computers, smartphones, and other advanced technologies are being integrated into vehicles to help and automate driving operations.
According to Precedence Research, the global autonomous market size was estimated USD 121.78 billion in 2022 and is projected to hit around USD 2,353.93 billion by 2023, i.e. a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 35% within 10 years
Rising number of accidents because of human error has triggered the need for AI to invade the automobile sector, and so the need of automotive datasets to train these models has come into play…
What is ADAS and its applications
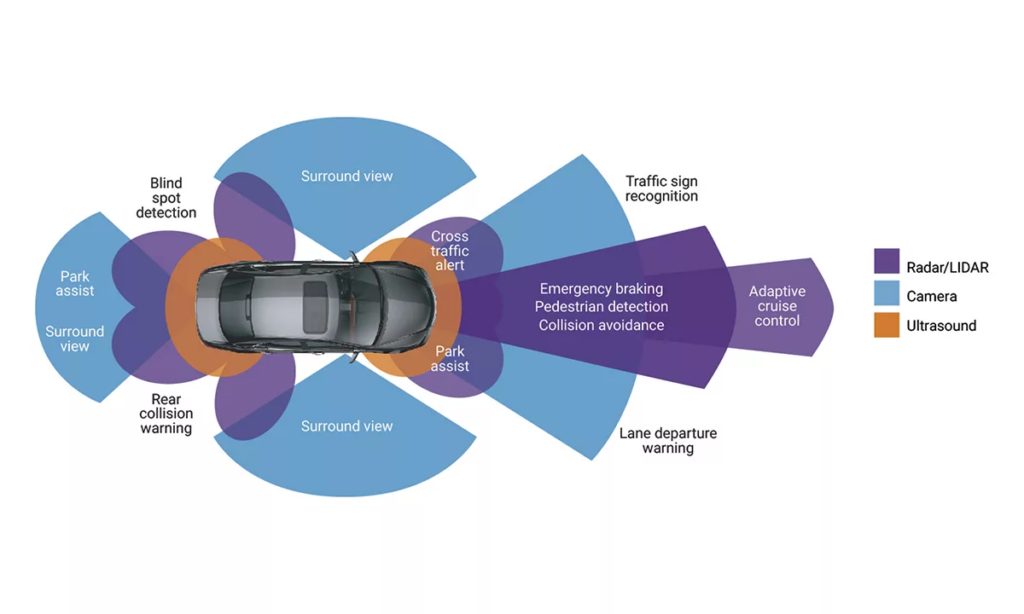
Known as Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems, are technological features that are designed to increase the safety of driving vehicles while informing the driver of various hazards. It can prevent a large number of unnatural deaths and injuries by reducing the number of car accidents and its serious impacts.
Essential safety-critical ADAS applications include:
- Pedestrian detection/avoidance
- Lane departure warning/correction
- Traffic sign recognition
- Automatic emergency braking
- Blind spot detection
Electronic Stability Control (ESC): Helps the driver maintain control of the vehicle in slippery conditions. It can also apply the brakes to the vehicle’s wheels to help keep it on track and prevent it from skidding uncontrollably
Adaptive cruise control: Highly-beneficial in stop-and-go traffic situations or highways, advanced cruise control can automatically accelerate, slow down, and at times stop the vehicle, depending on the action’s other objects in the immediate area.
Blind spot detection system: It is a system that uses sensors to detect vehicles in the driver’s blind spot and provide an audible or visual warning to the driver
Parking assistance: helps inform drivers of unseen areas so they know when to turn the steering wheel and stop. Vehicles equipped with rearview cameras have a better view of their surroundings than traditional side mirrors.
Glare-Free High Beam and Pixel Light: This new headlight application detects the lights of other vehicles and redirects the vehicle’s lights away to prevent other road users from being temporarily blinded. Its light uses sensors to adjust to darkness and the vehicle’s surroundings without disturbing oncoming traffic.
Lane departure warning system: Designed to alert drivers when their vehicle begins to veer out of its lane. This can happen for several reasons, including driver fatigue, distraction, or impairment. The system uses sensors to monitor the vehicle’s position and emits a warning sound or an indicator on the dashboard if it detects that the vehicle is veering out of its lane.
Use Cases we help
Data Annotation Techniques – Self Driving Cars
We help you with diverse labeling techniques after carefully studying your automotive project scope. We have a dedicated workforce trained for such complex annotation, QA teams that ensure 95%+ tagging accuracy levels, and tools to automate quality checks.

Bounding Box

3D Annotation

Semantic Segmentation

Polygon Annotation
View our SAMPLE DATASET
The MACGENCE Way
- TAT: Compliant high-quality data available at your disposal that comes with benefits of customization as well that can be quickly delivered
- QUALITY: Our dataset goes through rigorous 2-level quality checks before delivery
- COMPLIANCE: Adherence to both the mandatory compliances of HIPAA & GDPR
- ACCURACY: Provides gives ~90% accuracy across different annotation types and model datasets
- NO. OF USE CASES SOLVED: Experience across a diverse range of use cases
Building Smarter AI Together

Complainces